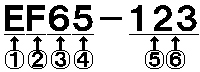Electric Trains
(Except Shinkansen
Bullet Trains) |
|
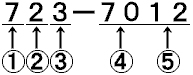
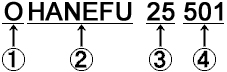
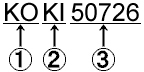
Example 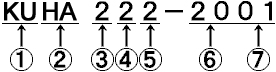
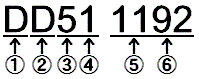
(1)=Type (2)=Usage (3)=Electric System (4)=Classification
(5)=Developed Order (6)=Classification Number (7)=Manufacturing
Number |
|
(1) Type |
This symbol shows if the car is equipped with a motor or a cab.
|
Symbol |
Type |
Example |
|
KUMO |
Motorized with
Cab |
KUMOHA, KUMORO, KUMOYA. |
|
MO |
Motorized |
MOHA, MORO, MOHANE |
|
KU |
Cab |
KUHA, KURO, KURU |
|
SA |
Accompany car |
SAHA, SARO, SAHASI |
|
Basic type are MO, KU and SA.
Car with a cab is equipped with a motorman's seat and is basically the car
at both ends.
Accompany car would be a car without a motor or a cab. |
|
(2) Usage |
This symbol shows what the car is used for.
|
Symbol |
Usage |
Example |
|
RO |
First class |
KUMORO, MORO, KURO, SARO |
|
HA |
Normal class |
KUMOHA, MOHA, KUHA, SAHA |
|
RONE |
First class Sleeping car |
SARONE |
|
HANE |
Normal class Sleeping car
|
MOHANE, KUHANE, SAHANE |
|
SI |
Dining car |
SAHASI |
|
NI |
Luggage car |
KUMONI |
|
YA |
Crew car |
MOYA, SAYA |
|
YU |
Mail car |
KUMOYUNI |
|
RU |
Storage car |
KUMORU, KURU |
|
Symbols may be combined with (1)Type and (2)Usage. For example, SAHASI, KUMOYUNI... |
|
(3) Electric System |
This symbol shows which electric is used for the car.
|
Number |
Type |
Example |
|
1 -3 |
Direct current
(can only run on Direct current section) |
Series 103, 221, 381 |
|
4 - 6 |
Direct and Alternating current
(equipped with an inverter and can run on both sections)
|
Series 485, 521, 683 |
|
7 - 8 |
Alternating current
(can only run on Alternating current section) |
Series 731, 787, 813 |
|
9 |
Trial car |
Series 991 |
|
|
|
(4) Classification |
This symbol shows what type of train it is operated.
|
Number |
Type |
Example |
|
0 - 3 |
Normal train (Commuter train, Suburban train)
|
Series 103, 415, 221, E331 |
|
4 |
Working train (Inspection car, Rescue car) |
KUMOYA145 |
|
5 - 8 |
Express train |
Series E255, 373, 681 |
|
9 |
Trial train |
Series 991 |
|
|
|
(5) Developed Order |
This number is used as a developed order of the train
but this may not apply to newly developed trains. |
|
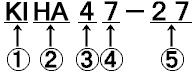
(6) Classification Number |
Depending on the operation area or manufacturing period, trains
have a classification number such as Type *000.
For example, Series 223 had the following classification number,
Type 0, Type 100, Type 1000, Type 2000, Type 2500, Type 5000 |
|
(7) Manufacturing Number |
Basically, manufacturing number is named starting from 1 with
its manufacturing order. |